Induction Motor:
With the rise of technology and evolution of ideas so far we have reached to certain extent is the extension of further development of implementation. So till now it's a lot to discuss about something that's inclusive of so many things. According to it one of such in science and technology is the invention of induction motor. Although there is an in between between discovery and invention but to me personally to have induction motor among us is an invention related to some discoveries. Induction motor was invented by a Serbian-American inventor Nikola Tesla. During his time there were not a bit of these modern technology to support him in implementing such a device to large extent. But with generation it came to be known as by a marvelous invention of him that has revolutionized today's advancement towards transportation, industrialization, machineries, etc.
Concept Of Induction Motor:
The principle of induction motor is all about the electromagnetic induction. The motor runs on a three phase power supply where each phase differs from the previous by 120 degree. When a three phase supply is given to the stator coil, the coil gets energized under each phase which generates a three phase magnetic flux. Now the rotor can be of two types: 1) Slip ring 2) Squirell cage. As soon as three phase flux is established it induces an emf in the rotor and current flows through the rotor as the rotor is shorted. Now the rotor current
 also creates its own magnetic flux that
also creates its own magnetic flux that
interacts with the stator flux producing
some torque to the rotor thereby rotation.
Now from this point of view it's interesting
to visualize and imagine the situations inside.
Initially the rotor remains at standstill
condition. But as soon as the stator produces
the magnetic flux it interacts the rotor causing
some current to flow thereby some torque.
This torque gives a starting rotation to the
motor. Now as the rotor speed slowly increases
it seems in relative to stator as if rotor speed is
reducing. On this flux cutting of the stator flux
 reduces and this leads to some variations of
reduces and this leads to some variations of
speed and torque in some relative sense.
Now lets visualize the situations of torque
and speed.
As the rotor achieves some starting torque
it starts rotating and with more speed the rotor
faces lesser frequency of flux cutting. This
reduces the induced rotor current frequency
as well as rotor flux frequency. As a result the
rotor current increases with reducing reactance
and that becomes maximum at certain speed
where the rotor torque also becomes maximum.
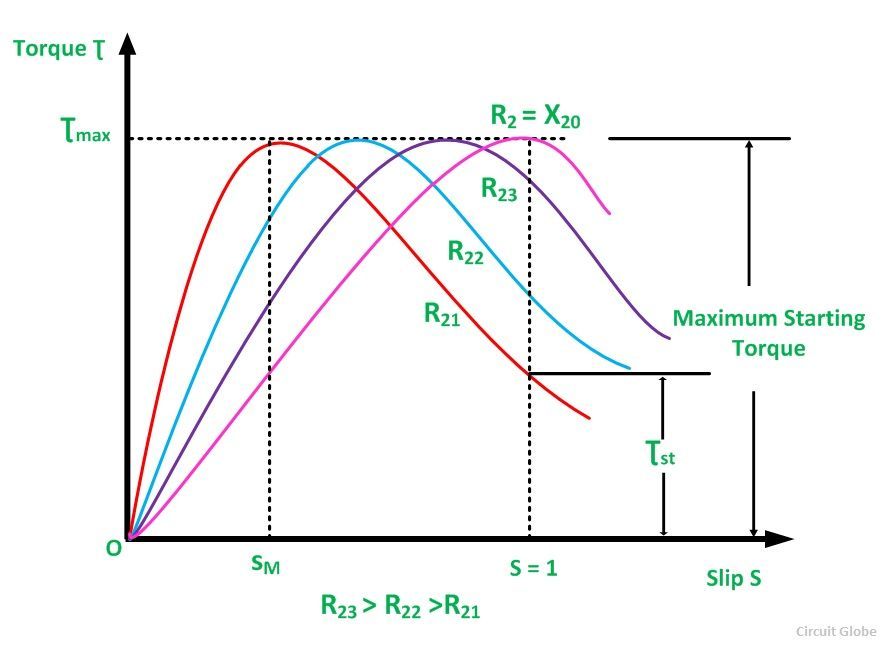 After that point of speed with more speed the
After that point of speed with more speed the
reduction of flux cutting gets a limit where it's
more dominating in a way to reduce the induced
current no matter whatever happens to rotor
reactance.Thus the induced current reduces
as well as induced flux and torque reduces.
With this the rotor speed reaches to a maximum
value based on the speed of the rotating stator flux
that has been established by the 50Hz three phase
supply which is known as synchronous speed.
Equations Related To The Induction Motor:
The equations are the doorway to the above explanation where
the physical parameters are arranged in terms of relative speed.
Ns= 120*f/p [Ns- synchronous speed, f- frequency, p-poles]
S=(Ns-Nr)/P [S- slip, Nr- rotor speed]
T=[ 3*(E20^2)/(2*pi*Ns)]*[s*R2/(R2^2 + s^2*X20^2)]
i.e based on this we can say, at s=0 or nearly synchronous speed condition,
Torque T is proportional to slip s as the rotor resistance is high compared to rotor reactance.
Below the max. torque it is,
Torque varies inversely with slip as inductive rotor reactance is very high compared rotor resistance.
Other Charecteristics Of Induction Motor:
Induction motor can be operated under three criterias of operation: 1)Motoring, 2)Breaking and 3)Generating.
Motoring:
The motoring operation is the normal running operation when 3 phase supply is given to its stator coils.Moreover it represents the incremental positive change in torque with respect to positive change in speed. In this condition power is drawn from the supply.
Breaking:
Breaking of induction motor prevails when direction of speed or rotation is reversed from forward motoring. Thus flow of rotor current reverses with the reverse of synchronous speed which counteracts the forward rotor motion.
Generating:
Now induction motor can act as a generator also. Once the rotor speed exceeds the stator synchronous speed then the rotor flux cuts the stator coil and more vigorously inducing emf to the stator coil. This causes the power flow from the motor to the supply. For an example the downhill motion of train.
With the rise of technology and evolution of ideas so far we have reached to certain extent is the extension of further development of implementation. So till now it's a lot to discuss about something that's inclusive of so many things. According to it one of such in science and technology is the invention of induction motor. Although there is an in between between discovery and invention but to me personally to have induction motor among us is an invention related to some discoveries. Induction motor was invented by a Serbian-American inventor Nikola Tesla. During his time there were not a bit of these modern technology to support him in implementing such a device to large extent. But with generation it came to be known as by a marvelous invention of him that has revolutionized today's advancement towards transportation, industrialization, machineries, etc.
Concept Of Induction Motor:
The principle of induction motor is all about the electromagnetic induction. The motor runs on a three phase power supply where each phase differs from the previous by 120 degree. When a three phase supply is given to the stator coil, the coil gets energized under each phase which generates a three phase magnetic flux. Now the rotor can be of two types: 1) Slip ring 2) Squirell cage. As soon as three phase flux is established it induces an emf in the rotor and current flows through the rotor as the rotor is shorted. Now the rotor current
 also creates its own magnetic flux that
also creates its own magnetic flux that interacts with the stator flux producing
some torque to the rotor thereby rotation.
Now from this point of view it's interesting
to visualize and imagine the situations inside.
Initially the rotor remains at standstill
condition. But as soon as the stator produces
the magnetic flux it interacts the rotor causing
some current to flow thereby some torque.
This torque gives a starting rotation to the
motor. Now as the rotor speed slowly increases
it seems in relative to stator as if rotor speed is
reducing. On this flux cutting of the stator flux
 reduces and this leads to some variations of
reduces and this leads to some variations of speed and torque in some relative sense.
Now lets visualize the situations of torque
and speed.
As the rotor achieves some starting torque
it starts rotating and with more speed the rotor
faces lesser frequency of flux cutting. This
reduces the induced rotor current frequency
as well as rotor flux frequency. As a result the
rotor current increases with reducing reactance
and that becomes maximum at certain speed
where the rotor torque also becomes maximum.
 After that point of speed with more speed the
After that point of speed with more speed the reduction of flux cutting gets a limit where it's
more dominating in a way to reduce the induced
current no matter whatever happens to rotor
reactance.Thus the induced current reduces
as well as induced flux and torque reduces.
With this the rotor speed reaches to a maximum
value based on the speed of the rotating stator flux
that has been established by the 50Hz three phase
supply which is known as synchronous speed.
Equations Related To The Induction Motor:
The equations are the doorway to the above explanation where
the physical parameters are arranged in terms of relative speed.
Ns= 120*f/p [Ns- synchronous speed, f- frequency, p-poles]
S=(Ns-Nr)/P [S- slip, Nr- rotor speed]
T=[ 3*(E20^2)/(2*pi*Ns)]*[s*R2/(R2^2 + s^2*X20^2)]
i.e based on this we can say, at s=0 or nearly synchronous speed condition,
Torque T is proportional to slip s as the rotor resistance is high compared to rotor reactance.
Below the max. torque it is,
Torque varies inversely with slip as inductive rotor reactance is very high compared rotor resistance.
Other Charecteristics Of Induction Motor:
Induction motor can be operated under three criterias of operation: 1)Motoring, 2)Breaking and 3)Generating.
Motoring:
The motoring operation is the normal running operation when 3 phase supply is given to its stator coils.Moreover it represents the incremental positive change in torque with respect to positive change in speed. In this condition power is drawn from the supply.
Breaking:
Breaking of induction motor prevails when direction of speed or rotation is reversed from forward motoring. Thus flow of rotor current reverses with the reverse of synchronous speed which counteracts the forward rotor motion.
Generating:
Now induction motor can act as a generator also. Once the rotor speed exceeds the stator synchronous speed then the rotor flux cuts the stator coil and more vigorously inducing emf to the stator coil. This causes the power flow from the motor to the supply. For an example the downhill motion of train.
Comments
Post a Comment